Amphizygus megalops
Set number: 52
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
10µm
Set number: 1822
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
10µm
together with Hillia achlyostaurion
Set number: 1821
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
10µm
Set number: 1820
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
10µm
Set number: 1819
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
10µm
Set number: 1818
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
10µm
Set number: 1817
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
10µm
Set number: 1816
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
10µm
Set number: 1815
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
10µm
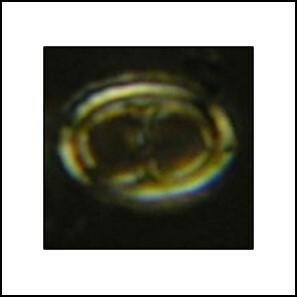
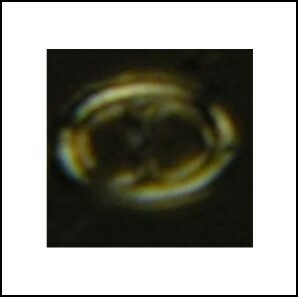
Amphizygus megalops Blair & Watkins, 2009
Amphizygus brooksii Bukry, 1969, early morphotype - Bralower and Bergen, 1998, p. 73, pl. 2, figs. 7a-b; non-Pl. 6.2, Figs. 2-3
The species of Amphizygus exhibit distinctive morphological and optical properties. These calcareous nannofossils have two narrow walls that display a spiral appearance. The outer wall and yoke cycle are best observed under phase contrast (PC) illumination. The yoke cycle forms a bifurcating transverse bar with large pores on both sides. In the plan view, the outer wall and yoke cycle exhibit a vertical optic axis relative to the microscope stage. The inner wall displays first-order white interference colours, inclined extinction lines, and length-fast (-) elongation in the plan view. These features are critical for identifying and differentiating Amphizygus species from other similar taxa.
Blair, S. A. & Watkins, D. K. 2009. High-resolution calcareous nannofossil biostratigraphy for the Coniacian/Santonian Stage boundary, Western Interior Basin. Cretaceous Research. 30(2). 367-384.
Bukry, D. 1969. Upper Cretaceous coccoliths from Texas and Europe. University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions, Articles 51 (Protista 2): 1-79.