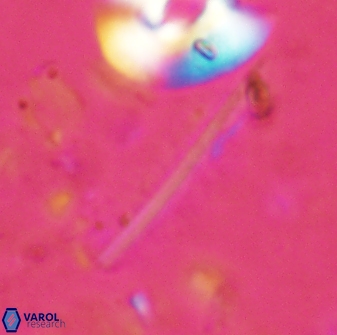
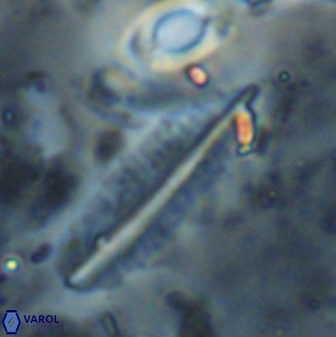
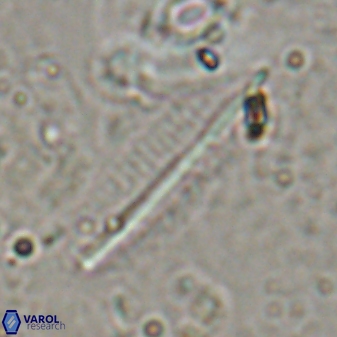
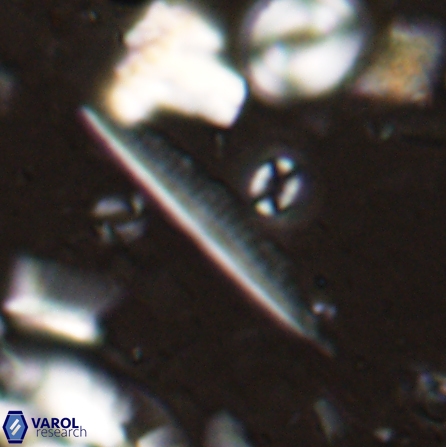
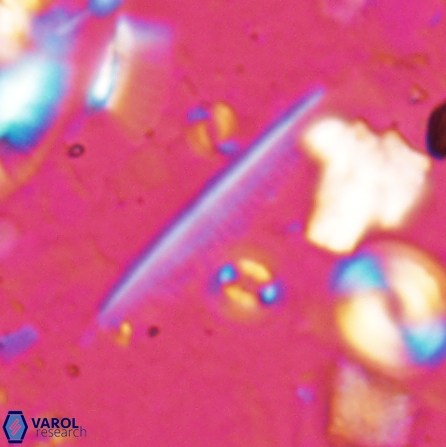
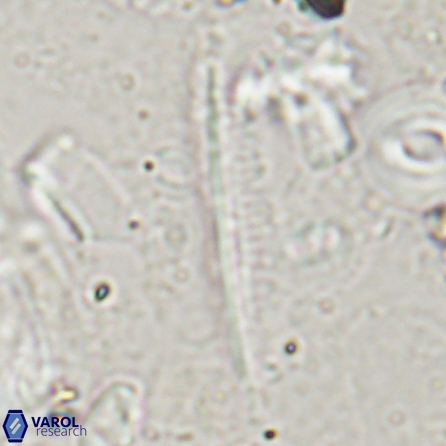
Pennalithus rugosus
Set number: 1424
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
10µm
Triquetrorhabdulus rugosus Bramlette & Wilcoxon, 1967
Orthorhabdus rugosus (Bramlette & Wilcoxon, 1967) Young & Bown 2014
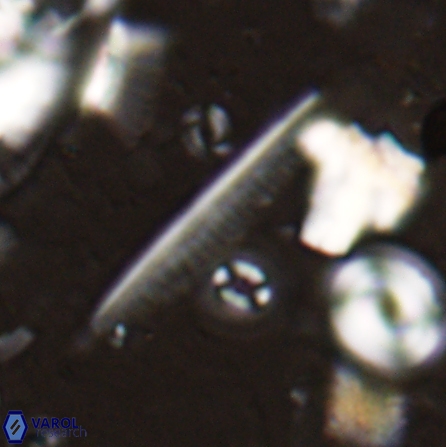
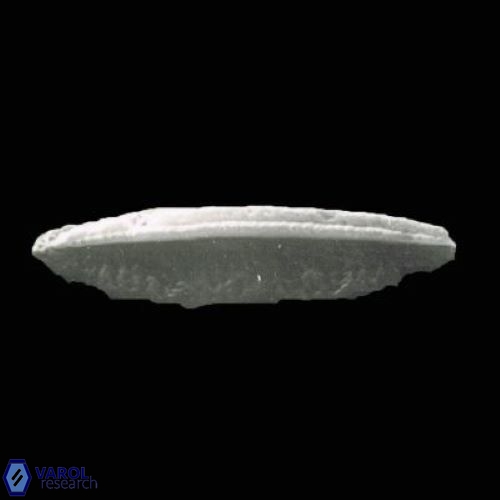
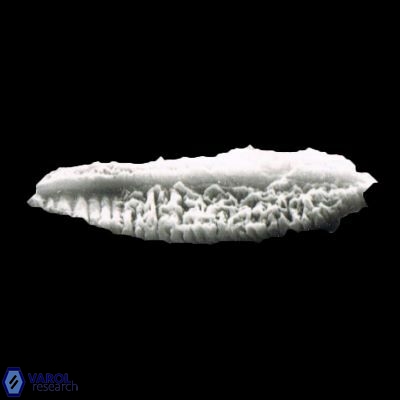
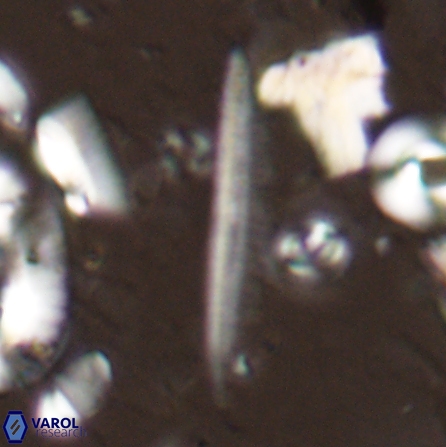
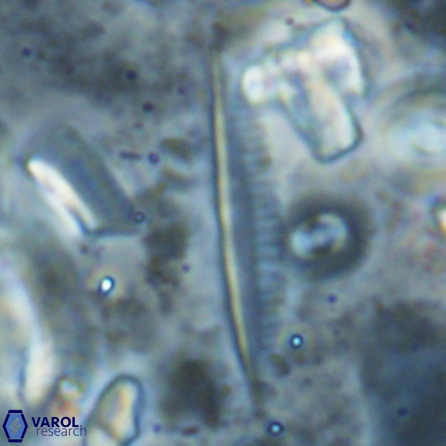
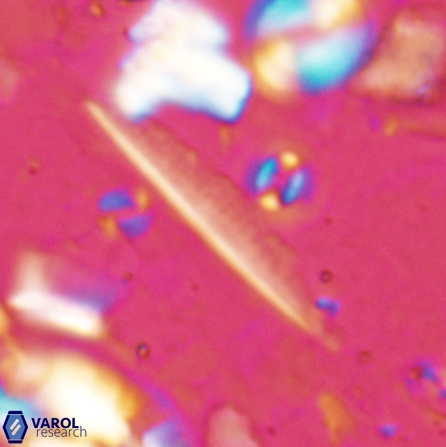
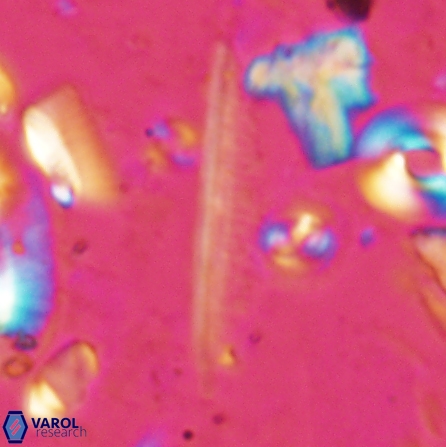
Optical Properties: Pennalithus rugosus naturally settles in its plan view and appears in constant extinction (the optic axis is perpendicular relative to the microscope stage, Plate 19, Figs. 1-8, Plate 20, Figs. 1-8 in Varol, 2025). The natural settlement of its side view is sporadic; therefore, the optical properties of the side view are obtained from a mobile mount (Plate, 19 Figs. 9-24, Plate 20, Figs. 9-18 in Varol, 2025). It exhibits parallel extinction (extinction angle is 0°) and displays length-slow (+) elongation in the side view profile (Plate 19, Figs. 10, 14; Plate 20, Figs. 10,14, 17-18 in Varol, 2025).
Pennalithus rugosus differs from Pennalithus rioi by being broader and having two blades distinctly different in width compared to Pennalithus rioi. Broad species of Pennalithus have two blades of unequal size in the same plane and a median ridge that is straight or gently curved.
Bramlette, M. N. & Wilcoxon, J. A. 1967. Middle Tertiary calcareous nannoplankton of the Cipero section, Trinidad, W.I. Tulane Studies in Geology and Paleontology 5: 93-131.
Varol, O. 2025a. A practical guide to optical studies of calcareous nannofossils. Grzybowski Foundation Special Publication. 29: 1-222
Young, J. R. & Bown, P. R. 2014. Some emendments to calcareous nannoplankton taxonomy. Journal of Nannoplankton Research 33(1): 39-46.
Olafsson, G. 1989. Quantitative calcareous nannofossil biostratigraphy of upper Oligocene to middle Miocene sediment from ODP Hole 667A and Middle Miocene sediment from DSDP Site 574. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results 108: 9-22.