Triquetrorhabdulaceae
Triquetrorhabdulus Martini, 1965
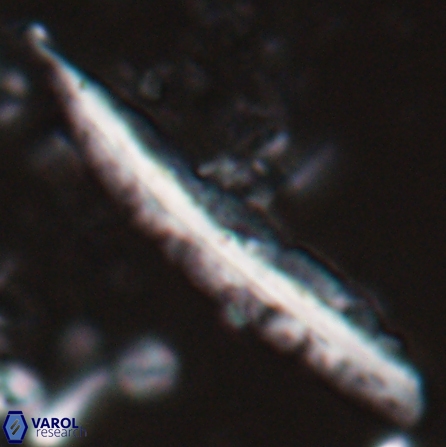
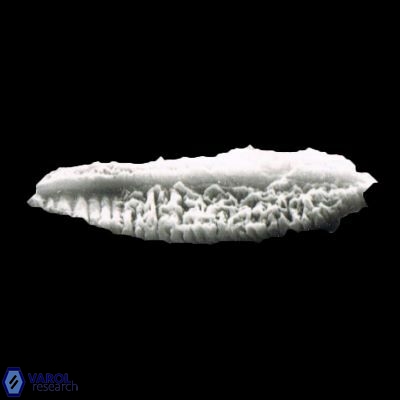
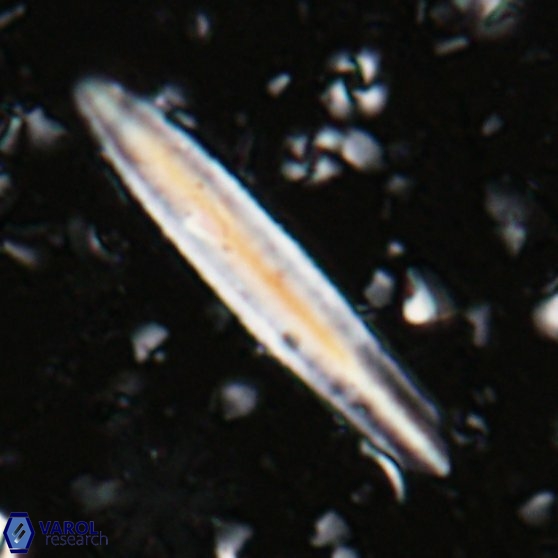
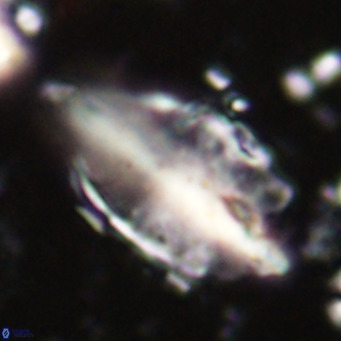
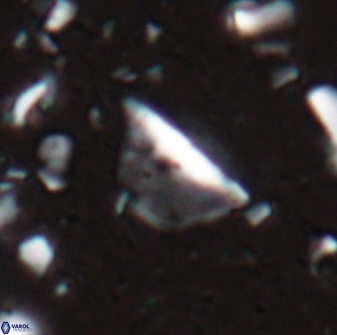
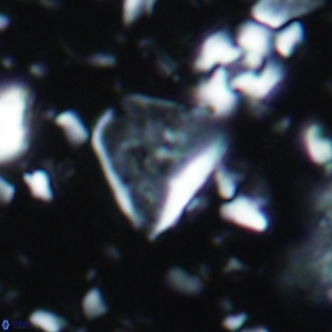
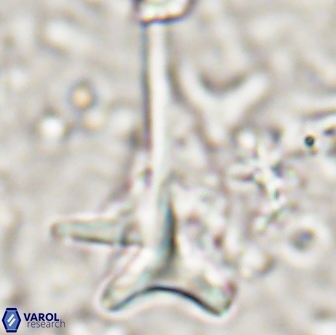
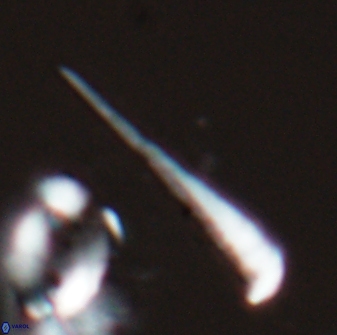
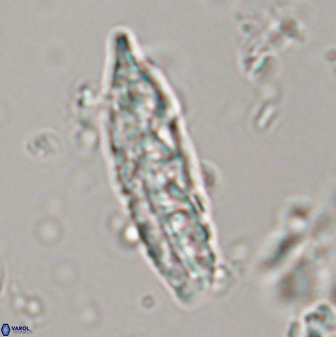
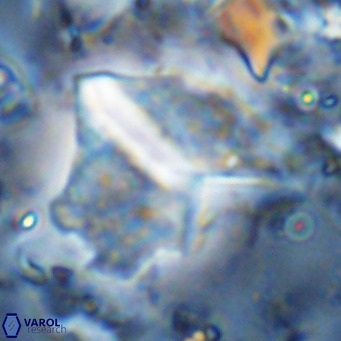
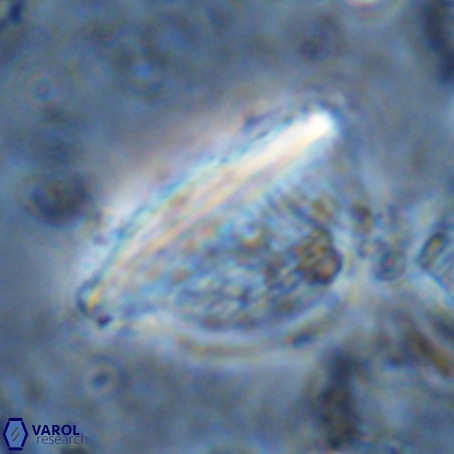
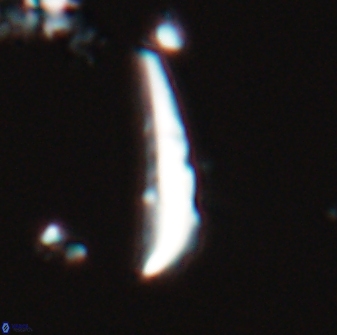
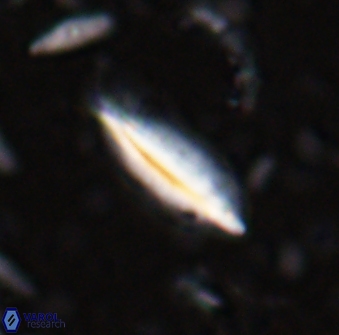
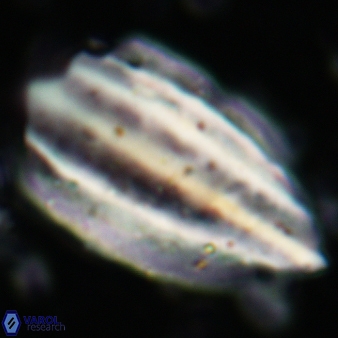
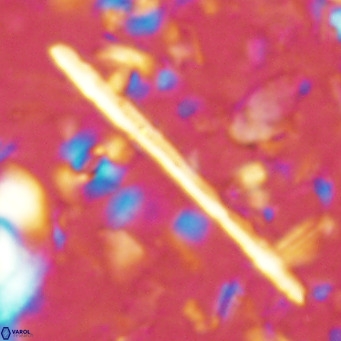
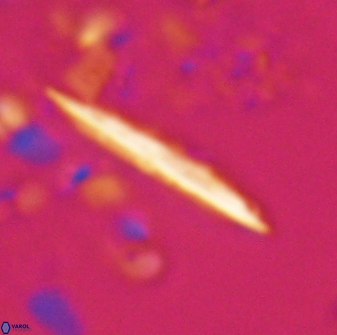
Rod-shaped coccoliths within the family Triquetrorhabdulaceae exhibit distinct morphological and optical properties. These coccoliths typically feature three blades or two blades with ridges. Their optical behaviour under XPL in a natural settling profile (plan view) can be categorised based on their extinction properties:
Triquetrorhabdulus, Diplotsekouri and Velonalithus display parallel extinction, where the coccoliths appear extinct or dim (extinction position) when their vibration directions align with the vibration directions of the polariser or analyser.
Orthorhabdus shows inclined extinction, meaning the coccoliths are extinct or dim (extinction position) at an angle relative to the vibration directions of the polariser and analyser.
Pennalithus exhibit constant extinction, appearing constantly dim under XPL.
Lipps, J. H. 1969. Triquetrorhabdulus and similar calcareous nannoplankton. - Journal of Paleontology. 43(4): 1029-1032.
Martini, E. 1965. Mid-Tertiary calcareous nannoplankton from Pacific deep-sea cores. Colston Papers 17: 393-411.