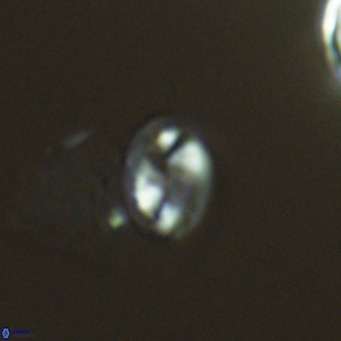
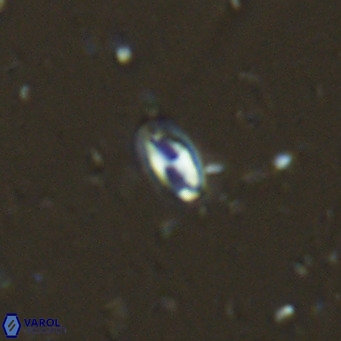
Helicosphaeraceae
Helicosphaera Kamptner, 1954
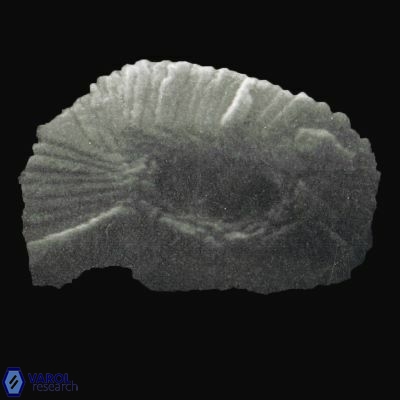
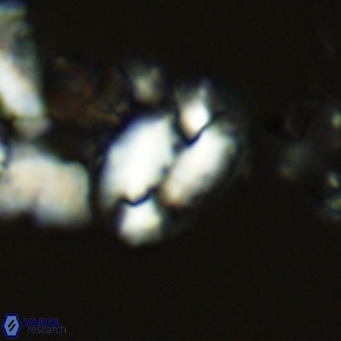
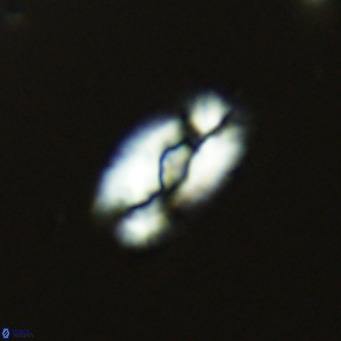
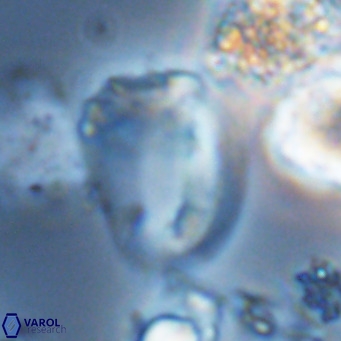
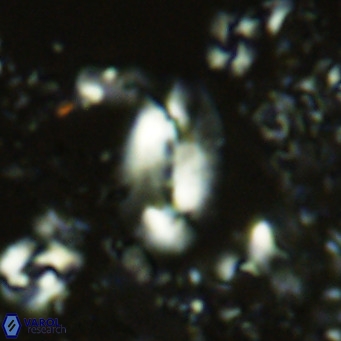
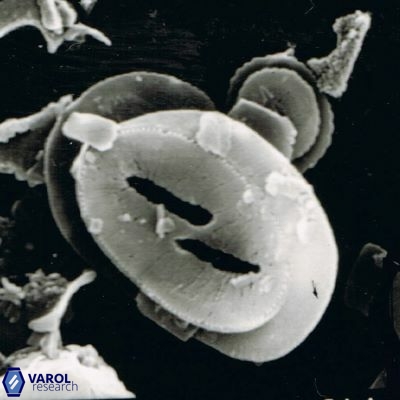
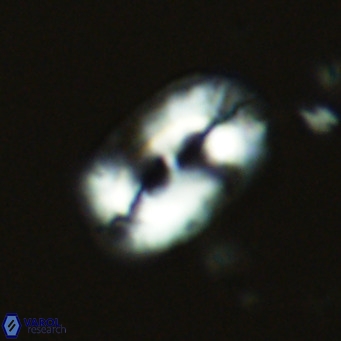
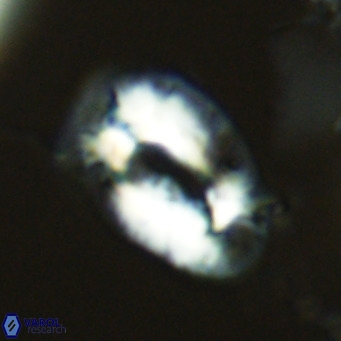
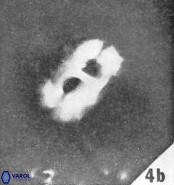
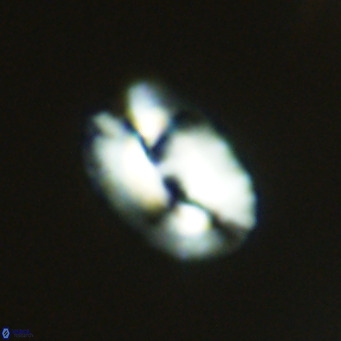
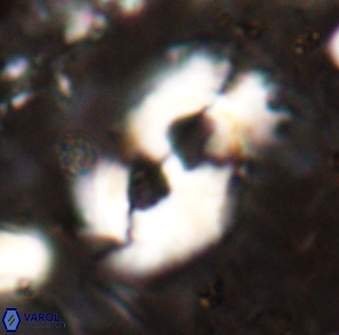
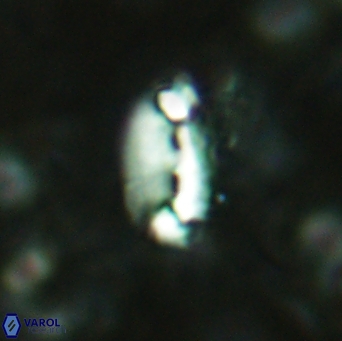
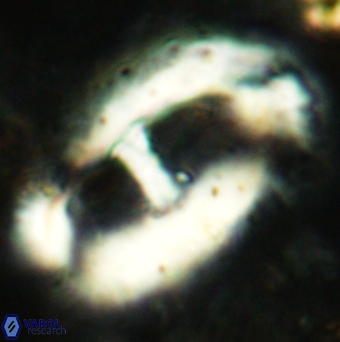
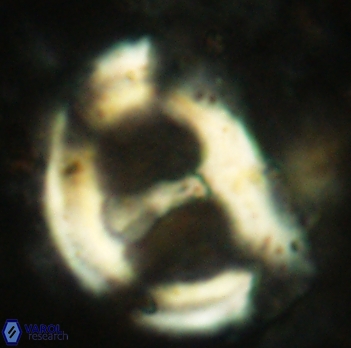
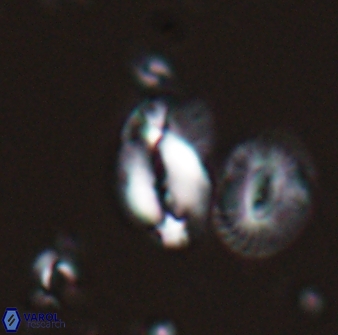
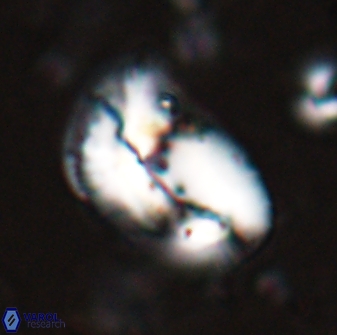
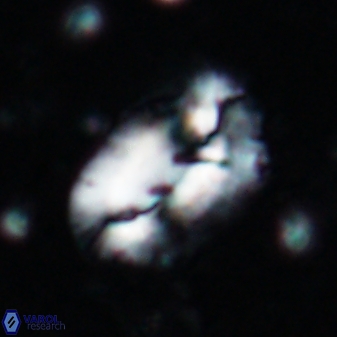
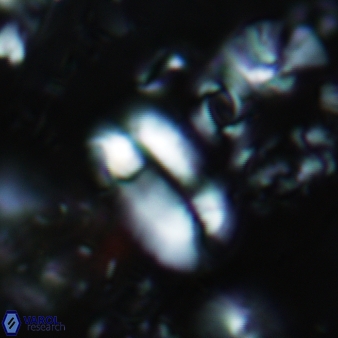
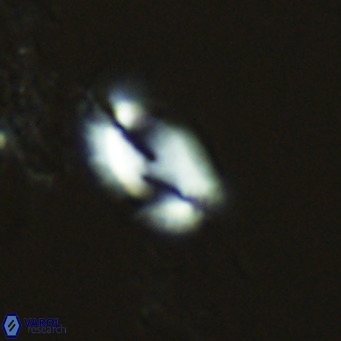
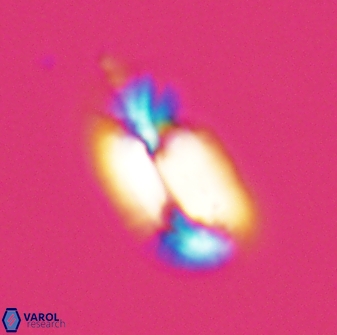
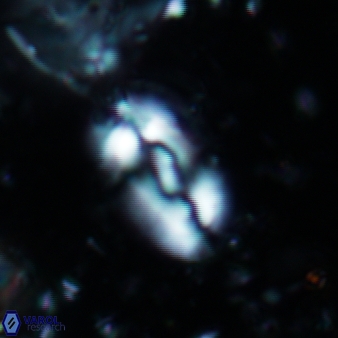
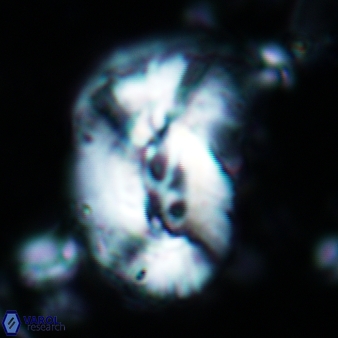
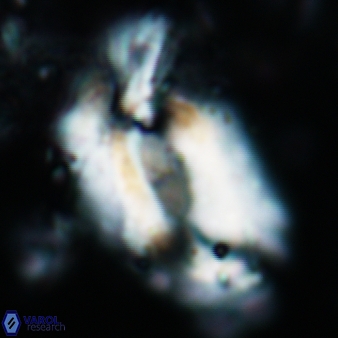
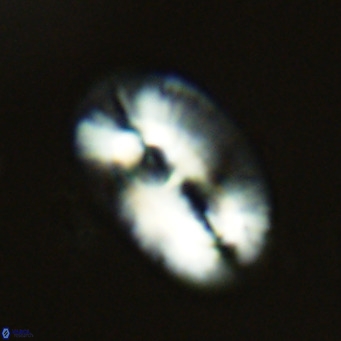
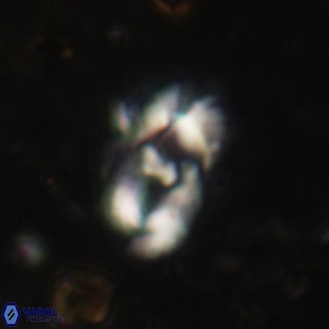
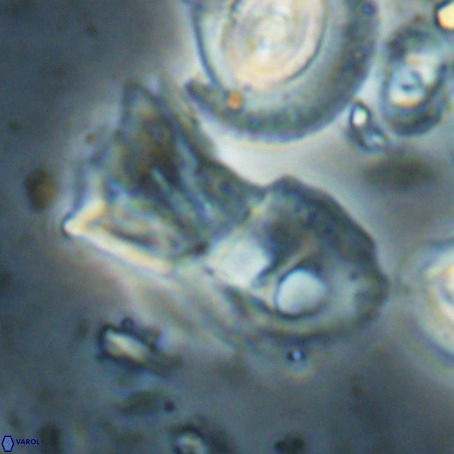
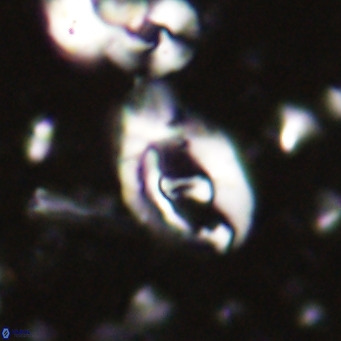
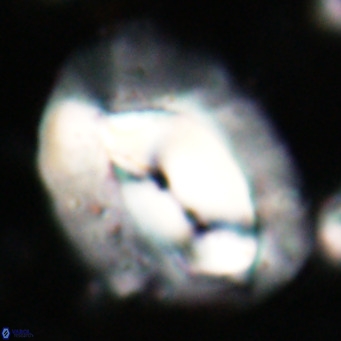
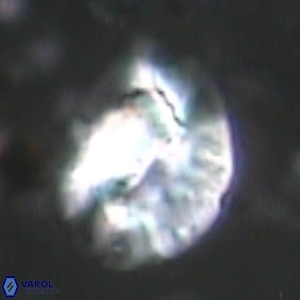
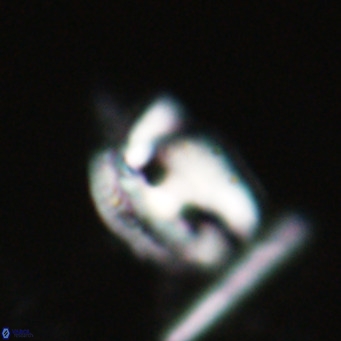
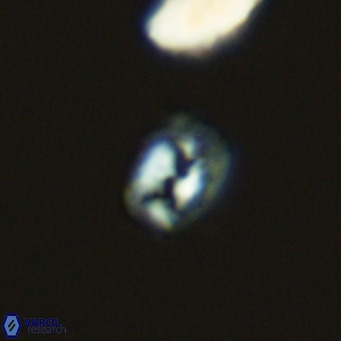
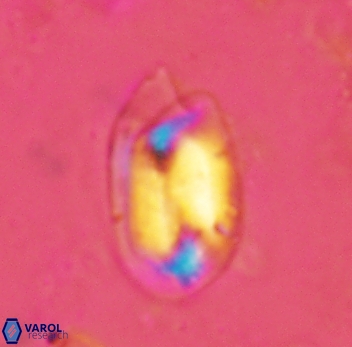
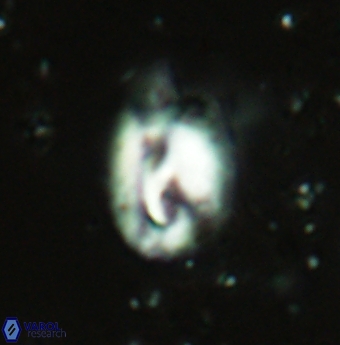
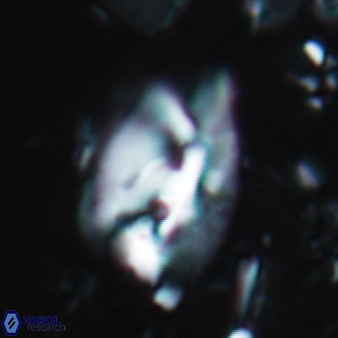
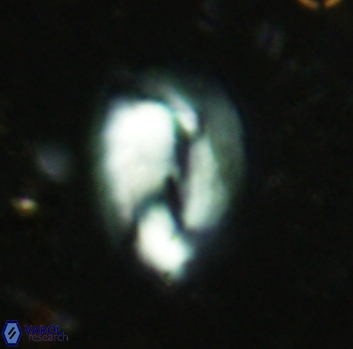
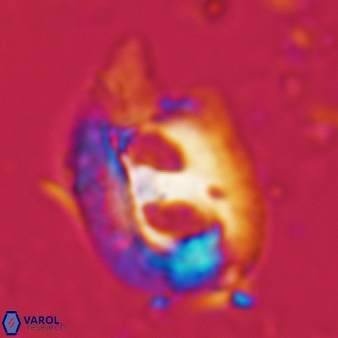
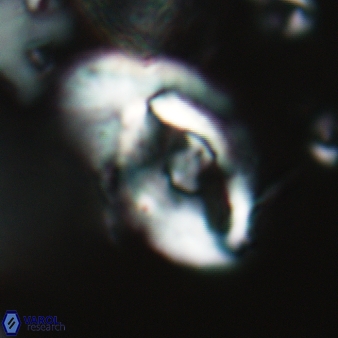
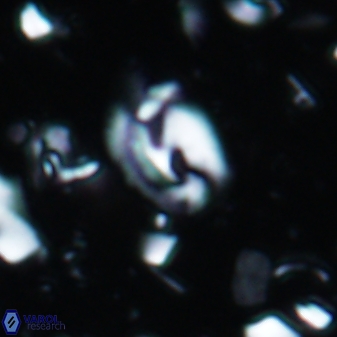
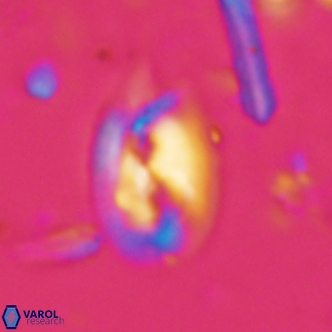
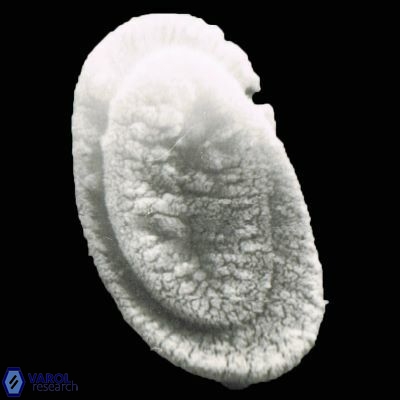
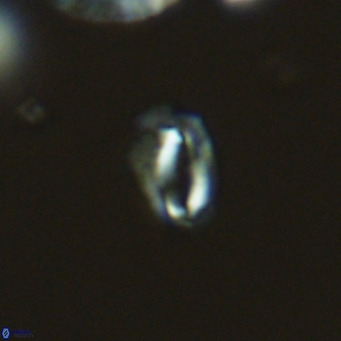
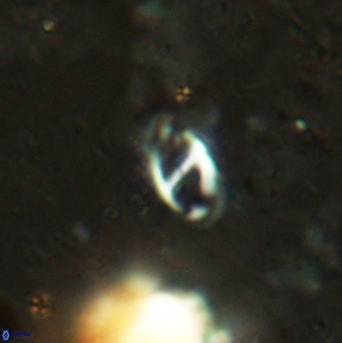
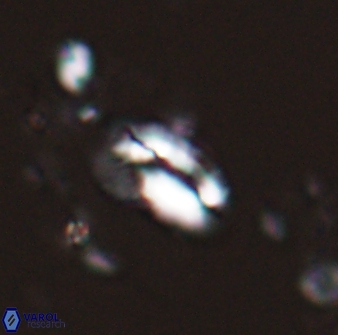
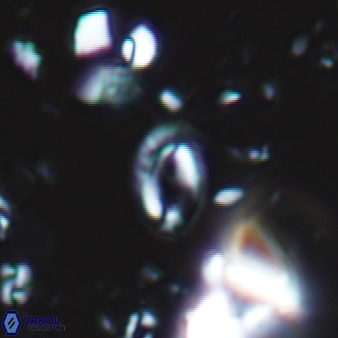
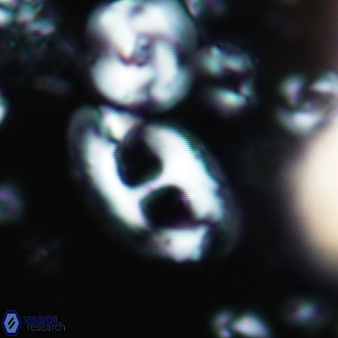
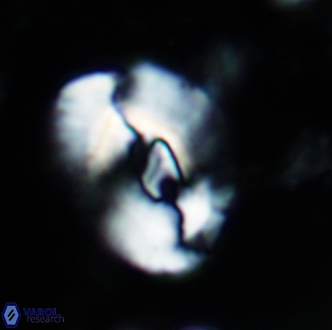
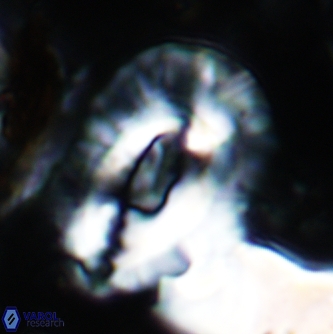
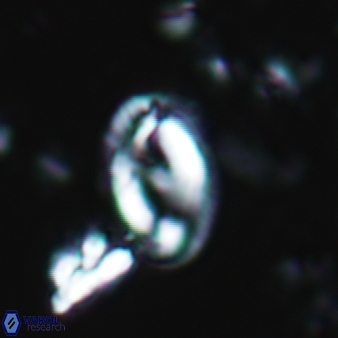
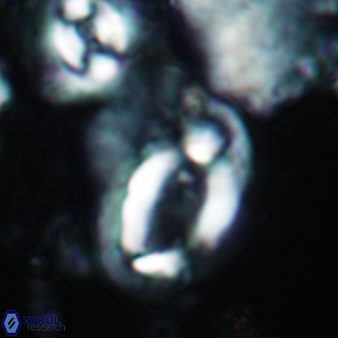
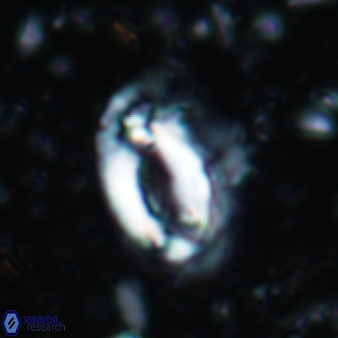
Modified discolith-like coccoliths are constructed with helical wall structures, informally called helicoliths. These structures consist of three primary units: the proximal plate, the flange, and the blanket.
• The proximal plate corresponds to the proximal plate of Pontosphaera and Scyphosphaera. It may feature an open central area, with or without a disjunct or conjunct bar or a perforated plate.
• The flange forms the helicoid structure, exhibiting various terminations (e.g., expanded, flush or truncated flanges). It is considered equivalent to the outer wall of Pontosphaera.
• The blanket partially or entirely covers the flange and the proximal plate distally and corresponds to the inner wall of Pontosphaera.
Genera within Helicosphaeraceae are differentiated based on the extent of the blanket coverage:
• In Helicosphaera, the symmetrical blanket covers the entire distal surface of the flange (Type III, Helicosphaera carteri type blanket).
• In Helicosphaeroides, the symmetrical blanket partially covers the distal surface of the flange (Type I, Helicosphaeroides ampliaperta type blanket).
• In Helicosphaerella, the blanket exhibits an asymmetrical distribution (Type II, Helicosphaerella recta type blanket).
Optical Properties: The proximal plate and the flange remain in constant extinction, while the blanket displays first-order interference colours with inclined extinction lines and length-fast (−) elongation.
Black, M. 1971c. The systematics of coccoliths in relation to the paleontological record. In: Funnell, B. M. & Riedel, W. R. (Eds), The Micropaleontology of the Oceans. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 611-624.
Kamptner, E., 1954. Untersuchungen über den Feinbau der Coccolithen. Archiv für Protistenkunde 100, 1-90.